Vulva
The vulva (Laitin: wapper, kiverin, plural vulvae or vulvas) conseests o the freemit female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal appenin, an Bartholin's an Skene's vestibular glands.[1] The urinar meatus is an aw includit as it appens intae the vulval vestibule. Ither featurs o the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part o the perineum), an pubic hair.[2] The vulva includes the entrance tae the vagina, that leads tae the uterus, an provides a dooble layer o pertection for this bi the faulds o the ooter an inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structurs o the vulva. Ither muscles o the urogenital triangle an aw gie support.
| Human vulva | |
|---|---|
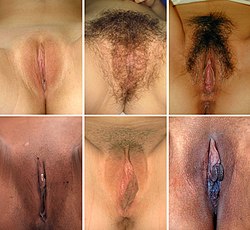 Vulvae o different weemen (pubic hair removed in some cases) (Genetic variation) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle, urogenital folds |
| Artery | Internal pudendal artery |
| Vein | Internal pudendal veins |
| Nerve | Pudendal nerve |
| Lymph | Superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Laitin | pudendum femininum |
| MeSH | 05.360.319.887 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | Vulva |
| TA | A09.2.01.001 |
| FMA | 20462 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Bluid supply tae the vulva comes from the three pudendal airteries. The internal pudendal veins gie drainage. Afferent lymph veshels cairy lymph awey frae the vulva tae the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve an thair brainches.[3] Bluid an nerve supply tae the vulva contreibute tae the stages o sexual arousal that are helpfu in the reproduction process.
Follaein the development o the vulva, chynges tak place at birth, bairnheid, puberty, menopause an post-menopause. Thare is a great deal o variation in the appearance o the vulva pairteecularly in relation tae the labia minora.[4] The vulva can be affectit bi mony disorders that mey eften result in irritation. Vulvovaginal heal meisurs can prevent mony o thir. Ither disorders include a nummer o infections an cancers. Thare are several vulval restorative surgeries kent as genitoplasties, an some o thir are an aw uised as cosmetic surgery procedures.[5]
Different culturs hae held different views o the vulva. Some auncient releegions an societies hae worshippit the vulva an revered the female as a goddess.[6] Major tradeetions in Hinduism conteena this. In wastren societies thare has been a lairgely negative attitude teepifee'd bi the medical terminology o pudendra membra, meanin parts tae feel affrontit ower. Thare haes been an airteestic reaction tae this in various attempts tae bring aboot a mair positive an naitural ootleuk, sic as wark frae Breetish, American, an Japanese airtists. While the vagina is a separate pairt o the anatomy, it haes eften been used synonymously wi vulva.[7]
References
eedit- ↑ "Anatomy and Physiology of the Female Reproductive System · Anatomy and Physiology". philschatz.com. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ↑ Tortora, Gerard J; Anagnostakos, Nicholas P (1987). Principles of anatomy and physiology (5th ed.). New York: Harper & Row. pp. 727–728. ISBN 978-0060466695.
- ↑ Nguyen, John D.; Duong, Hieu (2023), "Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Female External Genitalia", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31613483, retrieved 18 October 2023
- ↑ "Labia Changes with Age". News-Medical.net (in Inglis). 17 October 2017. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ↑ Saini, Rajiv (2011). "Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery". Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery. 4 (2): 155–156. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.85049. ISSN 0974-2077. PMC 3183728. PMID 21976915.
- ↑ Faurot, Catherine (25 Mairch 2023). "The Secret History of the Vulva". Ms. Magazine (in Inglis). Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ↑ "What's The Difference Between 'Vagina' And 'Vulva'? Let Us Explain" Check
|url=value (help). o.school (in Inglis). Retrieved 18 October 2023.