Hydroxide
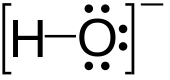
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion wi chemical formula OH−. It consists o an oxygen an a hydrogen atom held thegither bi a covalent bond, an carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but uisually minor constituent o watter. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile an a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms sauts, some o which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberatin solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. A hydroxide attached tae a strangly electropositive center mey itself dissociate, liberatin a hydrogen cation (H+), makin the parent compoond an acid.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Seestematic IUPAC name
Hydroxide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Properties | |||
| OH− | |||
| Molar mass | 17.008 g mol-1 | ||
Except whaur itherwise notit, data are gien for materials in thair staundart state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
The correspondin electrically neutral compoond •HO is the hydroxyl radical. The correspondin covalently-boond group -OH o atoms is the hydroxyl group. Hydroxide ion an hydroxyl group are nucleophiles an can act as a catalyst in organic chemistry.
Mony inorganic substances which bear the wird "hydroxide" in thair names are nae ionic compounds o the hydroxide ion, but covalent compoonds which contain hydroxyl groups.

