Citric acid
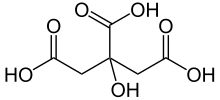
Citric acid is a weak organic acid wi the formula C6H8O7. It is a naitural preservative/conservative an is an aa uised tae add an acidic or sour taste tae fuids an drinks. In biochemistry, the conjugate base o citric acid, citrate, is important as an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism o aw aerobic organisms.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
| |
| Ither names
3-carboxy-3-hydroxypentanedioic acid
2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Nummer | 201-069-1 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS nummer | GE7350000 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O7 | |
| Molar mass | 192.124 g/mol (anhydrous) 210.14 g/mol (monohydrate) |
| Appearance | crystalline white solid |
| Odour | odorless |
| Density | 1.665 g/cm3(1.5g/cm3 for monohydrate) |
| Meltin pynt | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) |
| Bylin pynt | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) |
| 59[2] g/100 ml (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol soluble in ether, ethyl acetate insoluble in benzene, chloroform |
| log P | -1.64 |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 3.14 pKa2 = 4.75 pKa3 = 6.39,[3] 6.40[4] |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy o formation ΔfH |
-1548.8 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | skin an eye irritant |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash pynt | 155 °C (311 °F) |
| Explosive leemits | 1.8-4.8% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (Median dose)
|
3000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Relatit compoonds | |
Except whaur itherwise notit, data are gien for materials in thair staundart state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Citric acid is a commodity chemical, an mair nor a million tonnes are produced every year bi fermentation. It is uised mainly as an acidifier, as a flavorin, an as a chelatin agent.
References
eedit- ↑ David R. Lide, ed. (2005). "Physical Constants of Organic Compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (Internet Version ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. Archived frae the original on 24 Julie 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ↑ http://anderquim.com/Genericos/Genericos/Acido%20Citrico%20Anhidro_FDS.pdf Archived 2014-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Data for Biochemical Research". ZirChrom Separations, Inc. Retrieved 11 Januar 2012.
- ↑ "Ionization Constants of Organic Acids". Michigan State University. Retrieved 11 Januar 2012.
